
Antioxidants are often mentioned in everyday conversations.
This is true for both scholars and ordinary people.
You can find supplements that are sold in stores, and marketers and media especially love the health benefits they bring.
However, very few people really know what they are and how they work.
The concept of antioxidants is quite complex, but this article will explain in simple terms in a way that people can understand.
What are antioxidants and how do they work?
To understand the activity of antioxidants, we must start at the molecular level.
As you may know, all matter in the universe is made from .
Atoms are composed of cores containing protons and neutrons, and some electrons orbit the core.
This is a simple diagram of an atom:
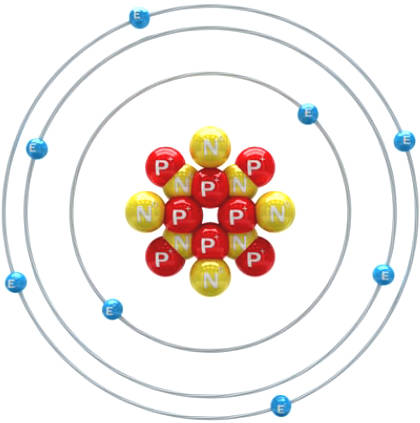
Blue balls are negatively charged electrons (-), while protons (red balls) in the core carry a positive charge (+).
When two or more atoms are connected, they become what we know about .
The human body is made up of substances like the protein , fat and DNA, are basically just big molecules with dozens, hundreds or thousands of atoms combined.
This is the image of a fatty acid molecule. Each ball represents an atom: 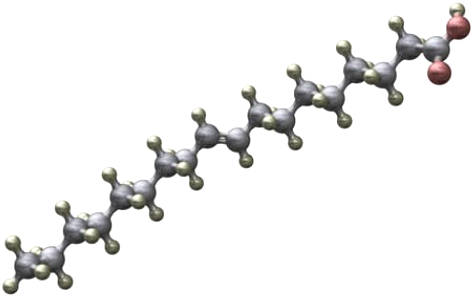
Humans and other organisms maintain their structure and function by chemical reaction. All chemical reactions needed to maintain life are collectively known
In these chemical reactions, larger molecules are broken down into smaller molecules, and smaller molecules are rearranged into larger molecules.
In order for a molecule to stabilize, it must contain the right amount of electrons. If the molecule suddenly loses an electron, it can turn into free radicals.
Free radicals are charged volatile molecules in the cell that can react with other molecules (like DNA) and damage them.
They can even form chain reactions, where molecules they harm also become free radicals.
This is how antioxidants come in: if a molecule loses an electron and turns into a free radical, the antioxidant molecule enters and "gives" an electron-free radical, neutralizing the molecule. that effectively.
This is how it happens: 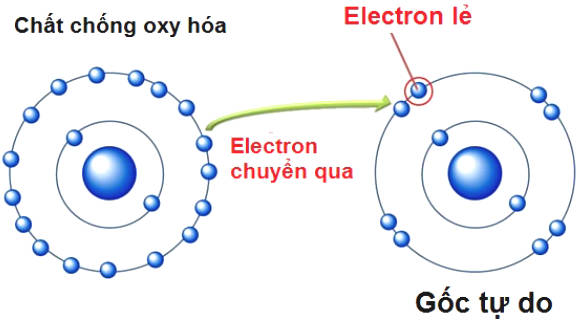
That is the mechanism behind antioxidants. They donate electrons to free radicals, disable them and prevent them from harming.
Summary: Antioxidants are molecules that resist damage from free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can harm cell structure. Antioxidants do this by putting electrons into free radicals and disabling them.
Antioxidants and free radicals are all important

Free radicals are constantly formed during metabolism.
Without antioxidants, they will destroy our bodies very quickly.
However, it is important to note that free radicals also serve important functions necessary for our survival .
For example, the body's immune cells use free radicals to kill the bacteria trying to attack us .
Just like a lot of activity inside the body, we need a certain balance. We need it's correct amount of free radicals and it's correct amount of antioxidants to control them.
When this balance is interrupted, everything can start going in the wrong direction.
When free radicals (substances capable of oxidizing) outperform substances anti oxidation, this can lead to a state called .
In the process of oxidative imbalance, important molecules in the body can be seriously damaged, sometimes even leading to cell death.
Some stressors and living habits are known to increase the formation of excessive free radicals and oxidative imbalance:
- Air pollution.
- Cigarette smoke.
- Drink alcohol.
- Toxic.
- High blood sugar .
- Consume a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids .
- Radiation, including excessive sunbathing.
- Bacterial, fungal or viral infections.
- Eat too much iron, magnesium, copper or zinc .
- Too little oxygen in the body .
- Too much oxygen in the body.
- High intensity and prolonged exercise, causing tissue damage .
- Eat too many antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E .
- Lack of antioxidants ( ).
Prolonged oxidative imbalance increases the risk of causing negative health consequences like cardiovascular disease and certain types of cancer. It is also thought to contribute to the aging process.
Summary: The body needs a certain balance between free radicals and antioxidants. When this balance is interrupted, it can lead to oxidative imbalance, causing a series of negative effects.
Antioxidants are essential for life and are found in all types of foods
Antioxidants are essential for the survival of all living organisms.
The human body even creates antioxidants, such as cellular antioxidants .
Both plants and animals, as well as all other life forms, have their own defenses against free radicals and damage caused by them.
Therefore, antioxidants are found in most all Foods derived from plants and animals.

Absorbing antioxidants from food is very important. In fact, our lives depend on the amount of antioxidants - specifically vitamin C and vitamin E.
Health benefits related to a diet rich in plants, or at least partly, are due to the variety of antioxidants they provide .
Meat and fish products also contain antioxidants , but with smaller amounts than fruits and vegetables. Berries are a particularly good source .
There are also many sources of abundant antioxidants, including green tea, the coffee and black chocolate .
According to some studies, coffee is actually the largest source of antioxidant in Western diets , but this is partly due to "normal" individuals who have not eaten a lot of foods rich in antioxidants.
Antioxidants can increase the lifespan of natural food products and processing. Therefore, they are often used as food additives . For example, vitamin C is often added to processed foods to act as a preservative.
Summary: Our diet is an essential source of antioxidants. They are often found in foods derived from plants and animals, especially vegetables, fruits and drinks such as coffee and tea.
Types of antioxidants in food

There are many different antioxidants found in food.
They can be classified into two groups, water-soluble antioxidants and fat-soluble antioxidants.
Water-soluble antioxidants act in the liquid inside and outside the cell, while fat-soluble antioxidants are primarily active in cell membranes.
Here is a list of some important antioxidants:
- Vitamin C: One of the most important water-soluble antioxidants and an essential food nutrient.
- Vitamin E: Fat-soluble antioxidants mainly play an important role in protecting cell membranes against oxidation.
- Flavonoids: A large group of antioxidants are found in plant foods. They have many beneficial effects on health .
Many substances that can act as antioxidants may also have other important functions.
Notable examples include curcuminoid in turmeric and oleocanthal in Pure olive oil . They act as antioxidants, but they also have strong anti-inflammatory activity .
Summary: There are many different types of antioxidants in the diet, including vitamins C and E, as well as flavonoids. These substances may support other functions not related to antioxidant activity.
Should you take an antioxidant supplement?

Consuming antioxidants from food is essential for optimal health.
However, more is not always better.
Excessive ingestion of isolated antioxidants may have toxic effects and may even enhance rather than prevent oxidative damage.
In fact, some studies have shown that high doses of antioxidants do increase mortality risk .
Therefore, you should avoid taking high-dose antioxidant supplements.
In addition, studies show that food reduces oxidative damage more than functional foods.
For example, a study using orange blood showed that it had significantly higher antioxidant power than freshwater with the same amount of vitamin C .
The truth is that food has hundreds (if not Thousands ) Different nutrients work together. Taking only one or two separated nutrients will not have the same effect.
The best (and healthiest) strategy to ensure sufficient antioxidant intake is a diet that contains a variety of vegetables along with other healthy eating habits.
However, low-dose supplements such as multivitamins can be beneficial if you are deficient in certain nutrients or cannot follow a healthy diet.
Main message
Eating a lot of antioxidants is an essential part of a healthy diet, but getting too many isolated antioxidants (via supplements) can be harmful in some cases.
Finally, the best way to ensure you have enough antioxidants is to eat real foods that include a lot of healthy fruits and vegetables.
