Milk is a nutrient-rich liquid formed in the breast of dairy cows, to nourish newborn calves in the first months of life.
There are a variety of cow's milk products, such as cheese, ice cream, butter and yogurt.
These foods are called dairy products and they are a major part of the modern diet.
The nutritional composition of milk is complex and contains most of the nutrients that the human body needs.
This is the common milk: 
Nutritional value
The table below contains detailed information about nutrients in milk .
| Amount | |
| Calories | sixty one |
| Country | 88% |
| The protein | 3.2 g |
| Carb | 4.8 g |
| Street | 5.1 g |
| Fiber | 0 g |
| Fat | 3.3 g |
| Saturated fat | 1.87 g |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.81 g |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.2 g |
| Omega-3 | 0.08 g |
| Omega-6 | 0.12 g |
| Trans fat | ~ |
Note that many dairy products are supplemented with vitamins, including vitamin D and A.
Milk protein

Milk is a source the protein cornucopia .
It has about 1 g of protein per ounce of milk (30.5 g), or 7.7 g in each cup (244 g).
Milk proteins can be divided into two groups based on water solubility.
Insoluble milk proteins are called caseins, while soluble proteins are called whey proteins.
Both of these milk protein groups are considered to have excellent quality, with high levels of essential amino acids and good digestibility.
Summary: Milk is a high quality protein source, divided into two types: casein and whey.
Casein
Casein accounts for the majority of milk protein (80%).
Casein is actually a group of different proteins and the most common type is alpha-casein.
An important feature of casein is its ability to increase mineral absorption, such as calcium and phosphorus .
Casein also supports lowering blood pressure .
Summary: Casein accounts for the majority of milk protein and has many health benefits.
Whey protein
Whey is another protein family, accounting for 20% of the protein in milk.
Whey is especially rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), such as leucine, isoleucine, and valine.
It includes many soluble proteins with different properties.
Whey protein has been linked to many health benefits, such as lowering blood pressure and improve mood during times of stress .
Consuming whey protein is good for muscle growth and maintenance. Therefore, it is a popular supplement for athletes and athletes.
Summary: Whey protein is one of the two main protein groups of milk. In addition to being good for muscle growth and maintenance, they can lower blood pressure and improve mood.
Fat in milk

Whole milk is taken directly from cows containing about 4% fat.
In many countries, dairy marketing is based primarily on fat content. In the US, whole milk contains 3.25% fat, while fat-free milk is 2% and low-fat milk is 1%.
Milk fat is one of the most complex natural fats, containing about 400 different types of fatty acids .
Whole milk contains a lot of saturated fat. About 70% of the fatty acids in milk are saturated.
Polyunsaturated fats make up only a small amount, about 2.3% of total fat.
The remaining is monounsaturated fat, which accounts for about 28% of total fat.
Summary: Unprocessed milk contains 4% fat, but the fat content of commercial milk varies by type. Milk fat mainly consists of saturated fat.
Trans fat of ruminants
Trans fat is found naturally in dairy products.
Contrary to trans fat found in processed foods, trans fat in milk, also known as ruminant trans fat, is often considered to be healthy.
Milk contains a small amount of trans fat, such as vaccenic acid and conjugated linoleic acid, also known as CLA .
CLA has attracted considerable attention due to its various health benefits .
However, large doses of CLA through supplements may have harmful effects on metabolism .
Summary: Milk contains a small amount of trans fat from ruminants. Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is the most studied and is associated with a number of health benefits.
Carb
Carb milk is mainly in the form of simple sugars called lactose, which accounts for about 5% of milk weight.
In the digestive system, lactose is broken down into glucose and galactose. These are substances absorbed into the blood, and galactose is converted into glucose in the liver.
Some people lack the enzymes needed to break down lactose. This condition is called lactose intolerance.
Summary: In milk, carb makes up about 5%, mostly lactose (milk sugar) that many people cannot tolerate.
Vitamins and minerals

Milk contains all the vitamins and minerals needed to maintain the growth and development of young calves in the first months of life.
Milk also contains most of the essential nutrients for humans, making it one of the most nutritious foods on the planet.
The following vitamins and minerals are found in large amounts in milk:
- Vitamin B12: This essential vitamin is found only in foods of animal origin , and milk is rich in B12 .
- Calcium: Milk is not only one of the best sources of calcium, but calcium in milk is also easily absorbed .
- Riboflavin: One of the B vitamins, also known as vitamin B2. Dairy products are the largest source of riboflavin in the Western diet .
- Phosphorus: Dairy products are good sources of phosphorus, a mineral that plays an essential role in many biological processes.
Milk rich in vitamin D
Getting rich is the process Minerals or vitamins for food products.
As a public health strategy, enrichment of dairy products with vitamin D is quite common and even mandatory in some countries .
In the US, a cup of milk rich in vitamin D (244 g) may contain 65% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin D .
Summary: Milk is a great source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, calcium, riboflavin, and phosphorus. It is often enhanced with other vitamins, especially vitamin D.
Hormone in milk
More than 50 different hormones are naturally present in cow's milk.
These hormones are important for the development of newborn calves .
Except growth factor 1 insulin variety , hormones in cow's milk are not effective in humans.
IGF-1 is also found in breast milk and is the only hormone known to be absorbed from cow's milk. It is related to growth and regeneration .
Growth hormone in cows is another natural hormone in milk in small amounts. It is only biologically active in cattle and is not effective in humans.
Summary: Milk contains a variety of hormones that promote the development of newborn calves. Only growth factor 1 insulin strain (IGF-1) is active in humans.
Bone health and osteoporosis
Proof a condition characterized by decreased bone density, is a major risk factor for fractures in the elderly.
One of the functions of cow's milk is to promote bone growth and the development of young calves.
Cow's milk seems to have a similar effect on adults and is associated with higher bone density .
High levels of calcium and high protein content in milk are two main factors that are thought to make this effect .
Summary: As a rich source of calcium, milk can increase mineral density in bones, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Other health benefits of milk
Milk is one of the most nutritious foods you can find.

It has been extensively studied and has some important health benefits.
Blood pressure
Abnormal high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Dairy products are associated with a lower risk of high blood pressure .
This is thought to be due to the unique combination of calcium, potassium and magnesium in milk .
Other factors in milk can also act as peptides formed during the digestion of casein, the main protein layer in milk .
Summary: Milk and milk products may help lower blood pressure.
Lactose intolerance
, also known as milk sugar, is the main carbohydrate found in milk.
In the digestive system, it is broken down into subgroups of glucose and galactose. However, this does not happen to everyone.
An enzyme called lactase is needed for the breakdown of lactose. Some people lose their ability to digest lactose after early childhood.
The inability to digest lactose is called lactose intolerance.
It is estimated that about 75% of the world's population is lactose intolerant . However, the proportion of people with lactose intolerance varies greatly depending on the genotype.
This figure shows the frequency of lactose intolerance in many parts of the world: 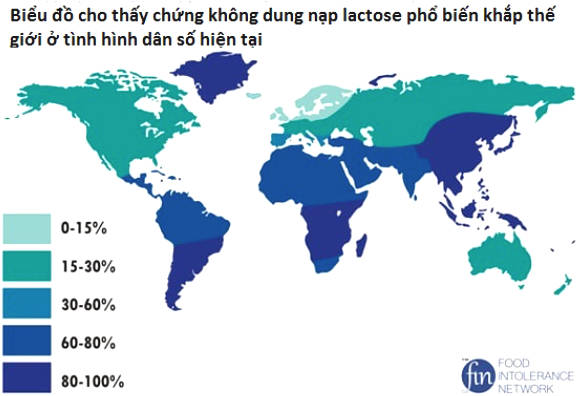
.
In people with lactose intolerance, lactose is not completely absorbed and some (or most) of it will go to the colon.
In the colon, the bacteria reside there ending the fermentation process. Fermentation leads to the formation of short-chain fatty acids and gases, such as methane and carbon dioxide.
Lactose intolerance is associated with many unpleasant symptoms such as heartburn, bloating, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
Summary: Many people do not tolerate milk sugar (lactose). The main symptoms are abdominal distention, flatulence, and diarrhea.
Other harmful effects
Milk consumption has a complex health impact.
Some ingredients in milk are beneficial, but some may have side effects.
Milk allergy
Milk allergies rarely occur in adults, but often occur in young children .
Usually, allergy symptoms are caused by whey proteins called alpha-lactoglobulin and beta-lactoglobulin, but they can also be caused by casein .
The main symptoms of milk allergy are skin rash, swelling, breathing problems, vomiting, diarrhea and blood in the stool .
Acne
Milk consumption is related to acne .
Acne is a skin disease caused by pimples, especially on the face, chest and back.
High consumption of milk increases insulin 1 growth factor (IGF-1) , hormones are thought to be related to the occurrence of acne .
Milk and cancer
Many observational studies have examined the association between consumption of dairy products and the risk of cancer.
In general, the evidence is inconsistent and very few conclusions are made from the data obtained.
However, quite a few studies show that consuming milk may increase the risk of prostate cancer in men .
In contrast, many studies have found a link between milk consumption and a reduced risk of colorectal cancer .
As a general recommendation, avoid excessive milk. The main problem is the need for moderation.
Summary: In addition to causing allergies to some people, milk has been linked to some side effects, such as an increased risk of acne and prostate cancer.
Treatment method

Almost all milk for human consumption is processed.
This increases safety in milk consumption and shelf life of dairy products.
Pasteurize
Sterilization is the process of heating milk to kill potentially harmful bacteria sometimes found in fresh milk .
Heat removes both harmful and beneficial bacteria, as well as yeast and mold.
However, sterilization does not make the milk sterile. Therefore it is necessary to quickly cool immediately after heating so as not to cause any viable bacteria to proliferate.
Sterilization will result in a loss of vitamins due to heat sensitivity, but does not have a significant effect on nutritional value .
Homogenization
Milk fat is made up of countless spheres of different sizes.
In fresh milk, these spherical fats tend to stick together and float to the surface of the milk.
Homogenization is the process of breaking fat globules into smaller units. This is done by heating the milk and pumping it through narrow pipes at high pressure.
The purpose of uniformity is to increase the shelf life of the milk while making the milk more wholesome and whiter.
Most dairy products produced from milk are homogeneous. An exception is cheese, often produced from heterogeneous milk.
Homogenization does not have any adverse effects on nutritional quality .
Summary: Commercial milk is sterilized and homogeneous to increase longevity and safety.
Fresh milk with pasteurized milk

Fresh milk is a term for unpasteurized or homogenous milk.
Sterilization takes place by heating milk to increase life expectancy and reducing the risk of disease from harmful microorganisms that may be present in fresh milk.
Heating will reduce some vitamins but this loss is not significant from a health point of view .
Homogenization is the process of breaking down fat globules in milk into smaller units, without harming health .
Consumption of fresh milk is associated with a lower risk of asthma in children, eczema and allergies . However, studies on this are small and no conclusions yet.
Although fresh milk is "more natural" than processed milk, its consumption is more risky.
In healthy cows, milk does not contain bacteria. It is the process of milking, transporting or preserving that milk is contaminated with bacteria, either from livestock itself or from the environment.
Most of these bacteria are harmless, and even beneficial, but occasionally infected milk can also cause illness.
Although the risk from drinking raw milk is very small, milk infections can have serious consequences.
Most people recover quickly, but people with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly or young children, are more likely to be affected.
In general, there is no strong evidence to support the consumption of fresh milk . Any potential health benefits may be reversed by health risks that may occur due to harmful bacterial infections.
Summary: Fresh milk is unpasteurized or homogenous milk. Drinking fresh milk is not recommended because it can be contaminated with harmful bacteria.
summary
Milk is one of the most nutritious drinks in the world.
It is not only rich in high quality protein but also a great source of vitamins and minerals, such as calcium, vitamin B12 and riboflavin.
For this reason, it may reduce the risk of osteoporosis and help lower blood pressure.
On the negative side, some people are allergic to milk proteins or milk sugar intolerances (lactose).
It is also associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer, but the evidence is quite weak.
Finally, moderate milk consumption can be healthy and need to avoid excessive consumption of milk.
