For decades, health authorities have always advised people to eat a low-fat diet.
At the time of giving instructions on low-fat diets, many people think that saturated fat is the main cause of heart disease.
This is the foundation of diet recommendations for the past few decades.

This is why big health organizations are always eliminating high-fat meat, eggs and dairy products, while targeting cereals, beans, fruits and vegetables (low in fat). , many carb).
These guidelines are based on unreliable evidence at the time, many respectable scientists have protested and argue that this could lead to unforeseen consequences.
Today, these recommendations are still completely unproven. Many high quality studies show that, in fact, there is not much significant relationship between saturated fat and cardiovascular disease .
However, these recommendations remain unchanged, although their scientific foundation has been removed.
Instructions on how to eat low fat and obesity epidemic
Instructions for eating less fat in 1977. Since then, the main and government health organizations have never changed its position.
Is this advice effective against obesity? The chart below can say everything.
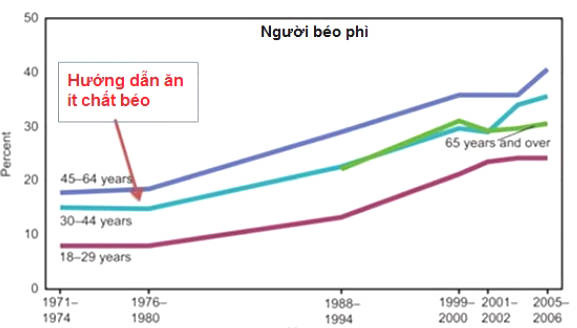
Of course, there are many things that are changing in society at the time and this chart does not prove that the above guidelines cause obesity epidemic, only that it starts at the time of the launch of the guidelines. on.
However, I personally think that imposing fat is harmful while turning green light on refined carb and sugar has a lot of problems.
Because many people think that this type of fat is the cause of diseases, low-fat junk foods have flooded the market.
These foods contain refined carb, sugar and HFCS, which are actually linked to heart disease, diabetes, obesity and all the diseases that low-fat diets are expected to treat.
Conclude: The low-fat diet guidelines were first introduced in 1977, at the same time as the obesity epidemic began.
The story of three major studies

Because the low-fat diet is supported by the government and all major health organizations, research on it has received a lot of financial resources.
Some great studies have learned about this diet and I want to discuss three of them below.
These are Very large, in which the participants are divided into two groups.
A group applies a low-fat diet, while the other group does not change anything and acts as a control group.
This is very good scientific evidence of the effectiveness of a low-fat diet.
Research for Women's Health (WHI)
Research started by the National Institutes of Health in 1991. Part of the study is to intervene in a low-fat diet to reduce obesity, cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Subjects of the study were 48,835 postmenopausal women, randomized in two groups of low-fat and control groups. Low-fat groups are instructed to eat less fat as well as increase consumption of fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
After 7.5-8 years, the low-fat group weighed less than 0.4 kg (!) Compared to the control group as well as no difference in risk of cardiovascular disease or cancer .
Risk Factor Intervention (MRFIT)
MRFIT is another large study of 12,866 men at high risk of heart attack. The results were published in 1982.
If someone can benefit from a low-fat diet (if it really works), that would be this group.
These men are required to quit smoking, eat less saturated fat and cholesterol, increase the consumption of vegetable oil (a typical low-fat diet). They did follow, but were not effective.
After 7 years of research, there was no difference in the rate of heart attack or death, although many men in the low-fat group quit smoking. Simply put, 100% fat diet is ineffective .
Diabetes Patient Action (Study The look AHEAD)
Actions for Health Patients with Diabetes are a deep lifestyle intervention study in patients with type 2 diabetes to reduce the rate of cancer, heart attack and stroke .
It is a study lasting 13.5 years, but they stopped when it was only 9.6 years because they found it ineffective.
The difference of this study is that it helps to lose weight by restricting strict calorie intake (total intake from 1,200 to 1,800 kcal per day) and increasing physical activity.
After 9.6 years, the group applied this weight decreased by 6%, compared with 3.5% in the control group. This difference is not too big, but quite remarkable.
The low-fat diet group lost weight and improved some aspects such as sleep apnea, activity and quality of life, but there was no difference in the risk of heart disease in groups (10). .
Low-fat diets seem to help with weight loss in diabetics, but only when accompanied by strict calorie exercise and restriction. Even with weight loss, it does not help patients live longer or have less heart disease.
Conclude: Long-term studies suggest that a low-fat diet generally does not reduce the risk of heart disease, cancer or other lifestyle-related diseases.
Low-fat diets adversely affect the biological indicator of blood

Although low-fat diets are organized like Recommended, but studies show they may adversely affect the risk factors for heart disease.
Perhaps you have heard about LDL also known as "bad" cholesterol. But that's only half the truth ... the size of LDL particles is the problem.
The more small particles the body has, the higher the risk of heart disease. If the majority is large, the risk of heart disease is low .
The problem with a low-fat diet is that it can alter the LDL from a large, benign LDL into a small, thick and harmful LDL seal .
Some studies have also shown that low-fat diets can lower HDL (good) cholesterol and increase blood triglycerides, another major risk factor .
Conclude: Low-fat diets can negatively affect risk factors for heart disease such as LDL, HDL and triglyceride granules.
Why isn't a low-fat diet effective?

There are several important parts of a low-fat diet that I think are effective.
For example, these diets emphasize reducing refined sugar consumption, replacing refined grains with whole grains and increasing consumption of vegetables.
These changes can lead to weight loss and help reduce the risk of heart disease. But why is it not effective?
It is because this diet is wrong at many important points.
Low-fat diet advocates a reduction in weight saturated fat which is mostly harmless .
It also supports increasing the amount of vegetable oil, which contributes to inflammation and increases the risk of heart disease .
Another side effect of reduced fat intake is to avoid eating animal foods such as meat and eggs, although they are rich in protein, give a long feeling of fullness and help with weight loss.
Perhaps a low-fat diet will really work if it does not recommend that people avoid consuming eggs and using a lot of vegetable oil.
