Vitamins can be classified based on their solubility.
Most vitamins are soluble in water, meaning they decompose in water. In contrast, fat-soluble vitamins are the same as in oil and do not decompose in water.
Fat-soluble vitamins are rich in fat-rich foods and are better absorbed into the blood when you eat them with fat. 
There are four fat-soluble vitamins in human diets:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
This article provides an overview of fat-soluble vitamins, health benefits, functions and major food sources.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A plays an important role in maintaining vision. Without it, you will be blind.
Classify
Vitamin A is not the only compound. Instead, it is a group of fat-soluble compounds called collectively .
The most common form of vitamin A in food is retinol. Other forms are retinal and retinoic acid found in the body but not or rarely in food.
(3,4-dehydroretinal) is an alternative, less active form found in freshwater fish .
Summary: Retinol is the main form of vitamin A in foods.
The role and function of vitamin A
Vitamin A supports many important aspects of body function, including:
- Maintain eyesight: People need vitamin A to maintain light receptors in their eyes and tear formation .
- Immune function: Vitamin A deficiency weakens immune function, increases the likelihood of infection .
- Body growth: Vitamin A is essential for cell growth. Deficiency can slow or prevent development in children .
- Hair grow: It is also very important for hair growth. Deficiency caused or hair loss .
- Reproduction function: Vitamin A maintains fertility and is very important for fetal development .
Summary: Vitamin A is best known for its important role in maintaining vision. It is also essential for body growth, immune function and reproductive health.
Food source
Vitamin A is found only in foods of animal origin. The main natural food sources are liver, fish liver oil and butter.
The table below shows some of the most vitamin A-rich food sources in 3.5 ounces (100 grams) : 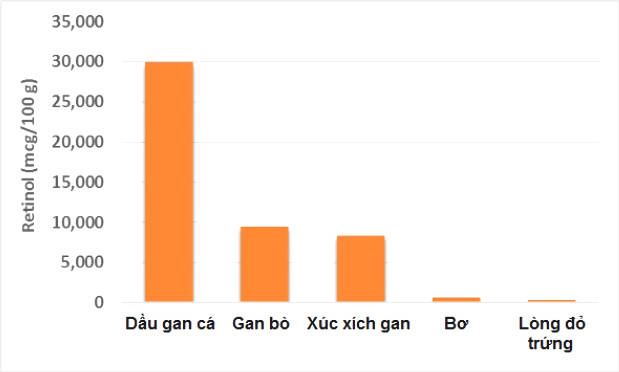
Vitamin A is also derived from some carotenoid antioxidants found in plants. They are referred to as vitamin A. precursors.
The most effective of these is beta-carotene, which is found in many vegetables such as carrots, kale and spinach .
Summary: The best sources of vitamin A include liver and fish oil. Vegetables also contain a lot of vitamin A carotene precursors, like beta-carotene.
Recommended amount
The table below shows the recommended daily intake (RDA) for vitamin A. RDA is the estimated amount of vitamin A that most people (about 97.5%) need for their daily needs.
This table also shows that acceptable upper consumption (UL), the highest daily consumption is considered safe for 97.5% of healthy people .
| RDA (IU / mcg) | UL (IU / mcg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Infant | 0–6 months | 1,333 / 400 | 2,000 / 600 |
| 7–12 months | 1,667 / 500 | 2,000 / 600 | |
| Children | 1–3 years | 1,000 / 300 | 2,000 / 600 |
| 4–8 years | 1,333 / 400 | 3,000 / 900 | |
| 9–13 years | 2,000 / 600 | 5,667 / 1700 | |
| Women | 14–18 years | 2,333 / 700 | 9,333 / 2800 |
| 19–70 years | 2,333 / 700 | 10,000 / 3000 | |
| male | 14–18 years | 3,000 / 900 | 9,333 / 2800 |
| 19–70 years | 3,000 / 900 | 10,000 / 3000 |
Summary: The recommended daily intake of vitamin A is 3,000 IU (900 mcg) for adult men and 2,333 (700 mcg) for women. For children, about 1,000 IU (300 mcg) to 2000 IU (600 mcg).
Vitamin A deficiency

Vitamin A deficiency rarely occurs in developed countries.
However, vegans may be at risk, because vitamin A is available only in animal-derived foods.
Although vitamin A precursors are abundant in fruits and vegetables but not always converted into effective retinol, this is the active form of vitamin A. The effectiveness of this conversion depends on human genetics .
Deficiencies are also common in some developing countries, where many types of food are limited. This usually happens in people who have the main diet of refined rice, white potatoes or cassava (cassava) that lack meat, fat and vegetables.
Common symptoms of early deficiency include night blindness. As it progresses, it can lead to more serious conditions, such as:
- Dry eyes: A serious deficiency can cause a characteristic dry eye condition due to reduced tear formation .
- Blind: Severe vitamin A deficiency can lead to complete blindness. In fact, this is one of the most common preventable causes of blindness in the world .
- Hair loss: If you are deficient in vitamin A, you may start losing hair .
- Skin problems: Deficiency leads to skin condition or snail .
- Poor immune function: Bad vitamin A status or deficiency causes easy infection .
Summary: Severe vitamin A deficiency can lead to blindness. Other symptoms include hair loss, skin problems and an increased risk of infection.
Vitamin A poisoning
Taking vitamin A overdose leads to an adverse condition called . It is rare, but can have serious health effects.
The main cause is due to excessive use of vitamin A from functional foods, liver or cod liver oil. Conversely, eating a lot of vitamin A precursors does not cause excess disorders.
The main symptoms and consequences of poisoning include fatigue, headache, irritability, stomach pain, joint pain, poor appetite, vomiting, blurred vision, skin problems and inflammation in the mouth and eyes .
It can also lead to liver damage, bone loss and hair loss. At extremely high doses, vitamin A can be fatal .
Maximum limit of consumption of 10,000 IU (900 mcg) per day should be avoided in adults.
Higher amounts, or 300,000 IU (900 mg) can cause excessive disorders of acute vitamin A in adults. Children may experience harms with much lower amounts .
Tolerance levels in each individual changed significantly. Children and people with liver disease such as cirrhosis and hepatitis are at high risk and need extra care.
Pregnant women should also be particularly careful, as high doses of vitamin A can harm an unborn baby. Low doses of 25,000 IU per day are related to birth defects .
Summary: High doses of vitamin A can lead to excess vitamin A disorders, which are associated with many symptoms. Pregnant women should avoid eating a lot of vitamin A because of the risk of birth defects.
Benefits of vitamin A supplements
While dietary supplements benefit people with deficiency, most people have enough vitamin A from the diet and do not need to supplement.
However, controlled studies suggest that vitamin A supplements may benefit some people even if their diets meet the basic requirements.
For example, vitamin A supplements may help treat measles in children .
They protect against measles pneumonia and reduce the risk of death by about 50-80%. Studies show that vitamin A works by inhibiting measles virus .
Summary: Functional foods mainly help people who are deficient in vitamin A. An exception is functional foods that can help treat children with measles as studies have shown.
Summary of vitamin A

Vitamin A, also called retinol, is a fat-soluble vitamin linked to vision and eye health.
The most abundant sources of vitamin A are liver, fish liver oil and butter.
It can also be derived from vitamin A carotenoid precursors found in red, yellow and orange vegetables, as well as some dark green leafy vegetables.
Vitamin A deficiency in developed countries is rare, but is most common in people on a less diverse diet, especially those who mainly eat rice, white potatoes and cassava.
Clinical symptoms of vitamin A deficiency include night blindness, and a severe deficiency can lead to complete blindness.
However, consuming enough vitamin A is important but too much can be harmful.
Pregnant women should be careful not to eat too much vitamin A because of the risk of birth defects.
Vitamin D

Known as sunshine vitamin, vitamin D is produced by skin when exposed to sunlight.
It is best known for its beneficial effects on bone health, and a deficiency makes it easy to break a bone.
Classify
Vitamin D is a general term used to describe some fat-soluble compounds.
Also known as calciferol, vitamin D has two main forms from food:
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol): Found in mushrooms and some plants.
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol): Found in animal-based foods, such as eggs and fish oil, sun-tanning also produces this vitamin.
Summary: Vitamin D has two types of food: vitamin D2, found in mushrooms and plants, and vitamin D3, found in foods of animal origin.
The role and function of vitamin D
Vitamin D has many roles and functions, but only a few are well studied. These include:
- Maintain bones: Vitamin D regulates the amount of calcium and phosphorus circulating in the blood, which are the most important minerals for bone growth and development. It promotes the absorption of these minerals from the diet.
- Adjust the immune system: It also regulates and enhances immune system function .
After absorption into the blood, the liver and kidney will convert calciferol into calcitriol, bioactive vitamin D form. It can also be stored for future use in the form .
Vitamin D3 converted to calcitriol is more effective than vitamin D2 .
Summary: One of the most important functions of vitamin D is maintaining calcium and phosphorus in the blood. It is beneficial for bone health by promoting the absorption of these minerals.
Source of vitamin D
Your body can produce the necessary amount of vitamin D if regularly exposed to sunlight .
However, many people spend less time in the sun or in closed clothes when exposed to the sun. Other people apply sunscreen to avoid sunburn is also reasonable. Although sunscreen is highly recommended, it reduces the amount of vitamin D produced by the skin.
Therefore, people often have to rely on diet to get enough vitamin D.
Very few natural foods contain vitamin D. The best food sources are fatty fish and fish oil, but ultraviolet-exposed mushrooms can also contain significant amounts.
The chart below shows sources of vitamin D-rich foods in 3.5 ounces (100 grams) : 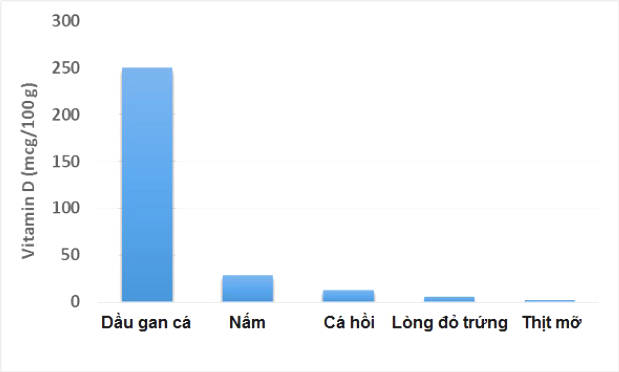
In addition, dairy products and margarine are often supplemented with vitamin D.
To learn more about the foods you can eat to increase your vitamin D intake, read this paragraph .
Summary: Your body can produce vitamin D if you regularly let most of your skin come into contact with sunlight. However, most people need to get it from a diet or supplement, such as fatty fish or fish oil.
Recommended amount
The table below shows the recommended daily intake (RDA) and the upper limit (UI) for vitamin D .
Since there is no RDA for babies, the values marked with an asterisk are sufficient amounts (AI). AI is similar to RDA, but based on weaker evidence.
| Age group | RDA (IU / mcg) | UL (IU / mcg) |
| 0–6 months | 400/10 * | 1,000 / 25 |
| 7–12 months | 400/10 * | 1,500 / 38 |
| 1–3 years old | 600/15 | 2,500 / 63 |
| 4–8 years old | 600/15 | 3,000 / 75 |
| 9–70 years old | 600/15 | 4,000 / 100 |
| 70+ years old | 800/20 | 4,000 / 100 |
If you want to learn more about optimal vitamin D levels, read this paragraph.
Summary: For children and adults, RDA for vitamin D is 600 IU (15 mcg). This amount is slightly higher in the elderly, 800 IU (20 mcg).
Vitamin D deficiency

Vitamin D deficiency Serious is rare, but there are also cases of slight deficiency or impairment in hospitalized and elderly people.
Risk factors for deficiency are dark skin color, old age, obesity, less exposure to the sun and diseases that reduce fat absorption.
The most known consequences of vitamin D deficiency are soft bones, weak muscles and an increased risk of fractures. This situation is called in adults and rickets in children .
Vitamin D deficiency is also associated with poor immune function, increased susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases .
Other signs of deficiency or impairment may include fatigue, depression, hair loss and a healthy wound.
Observational studies have also linked low vitamin D levels or deficiency with the risk of cancer death and high risk of heart attack .
Summary: The main symptoms of vitamin D deficiency include fatigue, muscle weakness, soft bones, increased risk of fractures and sensitivity to infection.
Vitamin D poisoning
Vitamin D poisoning is very rare.
While spending a lot of sun exposure without vitamin D poisoning, taking high-dose supplements can be harmful to you.
The main consequence of poisoning is a condition characterized by excessive calcium in the blood.
Symptoms include headache, nausea, poor appetite, weight loss, fatigue, heart and kidney damage, high blood pressure and fetal malformations.
It is often advised to avoid consuming the upper limit of vitamin D, which is 4,000 IU per day for adults.
Higher amounts, between 40,000 and 100,000 IU (1,000-2,500 mcg) daily can cause symptoms of poisoning in adults when taken daily for one or two months. Note that much lower doses may harm young children.
To learn more about the amount of vitamin D you can safely drink, read this paragraph.
Summary: Vitamin D poisoning in high doses. The most serious symptoms are dangerous high levels of calcium in the blood, which can harm the heart and kidneys.
Benefits of vitamin D supplements

Regular dietary supplements seem to prolong people's lives, especially elderly people who are hospitalized or living in nursing homes .
Functional foods may also reduce the risk of respiratory infections .
They may also have other benefits in people with vitamin D deficiency, but many studies need to be tested in people with enough vitamin D.
Summary: Health experts recommend that people take vitamin D supplements to prevent shortages. Supplements can improve general health and reduce the risk of infection.
Summary of vitamin D
Vitamin D is sometimes called sunshine vitamin. This is because your skin can produce enough vitamin D when it is sunny enough.
However, most people do not get enough vitamin D from the sun alone. In addition, very few natural foods contain a lot of vitamin D, making functional foods necessary.
Natural sources rich in vitamin D include fatty fish, fish oil and mushrooms are sun-dried or ultraviolet rays.
Vitamin D deficiency is often associated with osteoporosis in adults, or rickets in children. Both diseases manifest in brittle or soft bones.
Vitamin E
As a powerful antioxidant, vitamin E helps protect cells from premature aging and damage caused by these .
Classify
Vitamin E is a group of eight antioxidants that have a similar structure divided into two groups:
- Tocopherol: Alpha-tocopherol, beta-tocopherol, gamma-tocopherol and delta-tocopherol.
- Tocotrienol: Alpha-tocotrienol, beta-tocotrienol, gamma-tocotrienol and delta-tocotrienol.
Alpha-tocopherol is the most common form of vitamin E. It accounts for about 90% of vitamin E in the blood.
Summary: Vitamin E is a group of related compounds divided into tocopherol and tocotrienol. Alpha-tocopherol is the most common type.
The role and function of vitamin E

These antioxidant properties are enhanced by other nutrients, such as vitamin C, vitamin B3 and selenium.
In large amounts, vitamin E also acts as a blood thinner, reducing the likelihood of blood clots .
Summary: The important role of Vitamin E is to act as an antioxidant, protecting cells against free radicals and oxidative damage.
Food source
Foods rich in vitamin E include some vegetable oils, nuts and nuts. The chart below shows some of the best sources of vitamin E in 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of food : 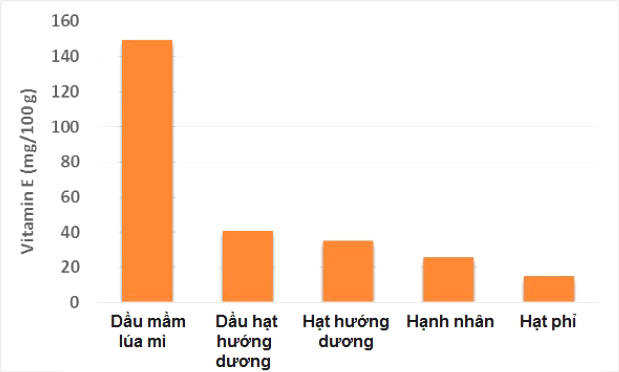
Other rich sources of vitamin E include avocado, peanut butter , margarine, fatty fish and fish liver oil.
Summary: The best source of vitamin E is vegetable oil, nuts and seeds.
Recommended amount
The table below shows the amount of RDA and the upper limit for vitamin E consumption. Values marked with an asterisk are sufficient amounts, because there is no value for RDA for infants.
| Age group | RDA (IU / mg) | UL (IU / mg) | |
| Infant | 0–6 months | 6/4 * | Unclear |
| 7–12 months | 8/5 * | Unclear | |
| Children | 1–3 years old | June 9 | 300/200 |
| 4–8 years old | July 11 | 450/300 | |
| 9–13 years old | November 17 | 900/600 | |
| Children | 14–18 years old | 23/15 | 1,200 / 800 |
| Adults | 19–50 years old | 23/15 | 1,500 / 1,000 |
| 51+ | December 18 | 1,500 / 1,000 |
Summary: In adults, the amount of RDA for vitamin E is 23 IU (15 mg). For children and adolescents, RDA ranges from 9 IU (6 mg) to 23 IU (15 mg), depending on the age group.
Lack of vitamin E
Vitamin E deficiency is uncommon and is never detected in healthy people.
It most commonly occurs in diseases that reduce fat absorption or vitamin E from food, such as cystic fibrosis and liver disease.
Symptoms of vitamin E deficiency include muscle weakness, difficulty walking, tremor, vision problems, poor immune function and paralysis.
Prolonged severe deficiency can lead to anemia, heart disease, severe neurological problems, blindness, memory loss, poor reflexes and inability to control physical activity .
Summary: Vitamin E deficiency is rare, but can cause muscle weakness, sensitivity to infections, neurological problems and poor vision.
Vitamin E poisoning

It is difficult to find an overdose of vitamin E from the absorption of natural food sources. Cases of poisoning are only reported after too many users from supplements.
However, compared with vitamins A and D, vitamin E overdose seems harmless.
It can dilute blood, counteract the effect of vitamin K and cause excessive bleeding. Therefore, people taking blood thinners should avoid taking large doses of vitamin E .
In addition, at doses greater than 1,000 mg per day, vitamin E may have an effect on oxidation. It means that it can become an antagonist with an antioxidant, potentially leading to .
Summary: Vitamin E causes less poisoning at higher doses than vitamins A and D. However, high doses can cause bleeding and oxidative imbalance.
Benefits and risks when consuming a lot of vitamin E or functional foods
Consuming a lot of vitamin E from food or dietary supplements is associated with a number of benefits.
A type of vitamin E, gamma-tocopherol, increases blood flow by promoting the expansion of blood vessels, potentially reducing blood pressure and the risk of heart disease .
Gramma-tocopherol supplements can also cause blood thinning as well as lower "bad" LDL cholesterol levels .
In contrast, other studies show that high-dose vitamin E supplements may be harmful, even if they do not cause obvious poisoning symptoms.
For example, observational studies suggest that taking vitamin E supplements is associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer and death of unknown causes .
With the potentially harmful effects of vitamin E supplements, they cannot be recommended. High-quality studies are needed before there are firm conclusions about the long-term safety of these supplements.
Summary: Vitamin E supplements can reduce the risk of heart disease, but the evidence is conflicting. Some studies show that supplementation is highly harmful and requires more research.
Summary of vitamin E

Vitamin E is a powerful group of antioxidants, most commonly alpha-tocopherol.
Its main function is to act as an antioxidant and protect the body's cells from free radical damage.
The best sources of vitamin E include vegetable oil, nuts and nuts. Deficiency is rare in healthy people.
Although dietary supplements may provide certain health benefits, not all scientists agree. The long-term safety of vitamin E supplements is a matter of debate.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K plays an important role in blood clotting. Without it, you run the risk of bleeding to death.
Classify
Vitamin K is actually a group of fat-soluble compounds divided into two main groups:
- Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone): Found in foods of plant origin, phylloquinone is the main form of vitamin K in the diet .
- Vitamin K2 (menaquinone): This vitamin K is found in foods of animal origin and fermented soy products such as natto. Intestinal bacteria in the colon also create vitamin K2 .
In addition, there are at least three types of multivitamins, including vitamin K3 (menadione), vitamin K4 (menadiol diacetate) and vitamin K5.
Summary: Vitamin K is a group of compounds. The main forms available in foods are vitamin K1, found in plant foods, and vitamin K2, found in animal-derived foods and fermented soy products.
The role and function of vitamin K
Vitamin K plays an essential role in gift of blood coagulation. In fact, the "K" stands for "koagulation," which means Danish to close.
However, vitamin K also has other functions, including supporting bone health and helping to prevent calcification of blood vessels, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease .
Summary: Vitamin K is important for blood clotting and bone health support.
Food source
Foods rich in vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) are green leafy vegetables, while vitamin K2 (menaquinone) is mainly found in animal-derived foods and fermented soy products.
The table below shows some of the main food sources containing vitamin K1 in 3.5 ounces (100 grams) : 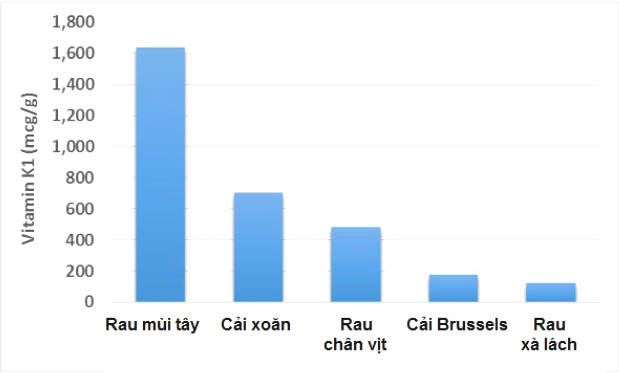
In contrast to phylloquinone, menaquinone is found only in small amounts in certain animal-derived and fat-rich foods, such as egg yolks, butter and liver.
It is also found in certain soy foods, such as natto.
Summary: Vitamin K1 is abundant in leafy vegetables, while vitamin K2 is found in low amounts in animal-derived foods and fermented soy foods.
Recommended amount
The table below shows the moderate intake (AI) for vitamin K.
AI is similar to RDA, daily consumption is said to meet the needs of 97.5% of people, but evidence-based AI is weaker than RDA.
| Age group | AI (mcg) | |
| Infant | 0–6 months | 2 |
| 7–12 months | 2.5 | |
| Children | 1–3 years old | 30 |
| 4–8 years old | 55 | |
| 9–13 years old | 60 | |
| Children | 14–18 years old | 75 |
| Women | 18+ | 90 |
| male | 18+ | 120 |
Summary: Moderate consumption (AI) of vitamin K is 90 mcg for women and 120 mcg for men. For children and adolescents, AI ranges from 30-75 mcg, depending on the age group.
Lack of vitamin K
Unlike vitamins A and D, vitamin K is not stored in the body in significant amounts. For this reason, consuming a vitamin K-deficient diet can lead to a deficiency for at least a week .
People who do not digest and absorb fat have the highest risk of vitamin K deficiency. This includes people with celiac disease, enteritis and cystic fibrosis.
Using broad-spectrum antibiotics may also increase the risk of deficiency, as well as high doses of vitamin A may reduce absorption of vitamin K.
High doses of vitamin E can also counteract the effects of vitamin K on blood clotting .
Without vitamin K, your blood will not coagulate or even a small wound can cause continuous bleeding. Fortunately, lack of vitamin K is very rare, because the body only needs a small amount to maintain blood clotting.
Low vitamin K levels are also associated with reduced bone density and increased risk of fractures in women .
Summary: Vitamin K deficiency can lead to excessive bleeding. Diseases that prevent fat absorption also increase the risk of deficiency.
Vitamin K poisoning
Unlike other fat-soluble vitamins, the natural forms of vitamin K are known to not cause poisoning.
Because scientists still have not established the upper limit of consumption for vitamin K, more research is needed.
In contrast, a form of multivitamins called menadione or vitamin K3, may have some side effects when consumed in high doses .
Summary: The maximum safe dose of vitamin K has not been announced and no symptoms of poisoning have been found.
Benefits of vitamin K supplements
Some controlled studies examined the effects of vitamin K supplements in humans. These studies show that vitamin K supplements - vitamin K1 and vitamin K2 - can reduce bone loss and bone fracture risk .
In addition, taking vitamin K2 supplements 45-90 mg daily helps increase the survival rate of liver cancer patients .
Observational studies also suggest that high vitamin K2 intake may reduce the risk of heart disease. However, evidence from controlled studies is limited and no conclusions .
Finally, taking 0.5 mg of vitamin K1 supplements daily for three years delayed the development of insulin resistance in the elderly compared to placebo. No significant differences were found in women .
Summary: Limited evidence suggests that vitamin K supplements can improve bone health, reduce the risk of heart disease and prolong the lives of liver cancer patients.
Summary of vitamin K

Vitamin K is a group of fat-soluble compounds divided into vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and vitamin K2 (menaquinone).
Vitamin K1 is mainly found in green leafy vegetables, while vitamin K2 comes from foods of animal origin such as liver, butter and egg yolk.
A small amount is also produced by intestinal bacteria in the colon.
Deficiencies weaken the ability of blood to clot, causing the risk of excessive bleeding.
There is little evidence of the health benefits of supplements in people who are not deficient. However, some controlled studies have shown that vitamin K supplements are beneficial for bone and heart health.
The bottom line
There are four fat-soluble vitamins in the human diet: A, D, E and K. They are essential for health and play important roles in the body.
Except vitamin D, most of them are easily obtained through a varied diet, especially if you eat a lot of seeds, nuts, vegetables, fish and egg .
These vitamins are often found in fatty foods and you can enhance their ability to absorb them by adding fat or oil to a low-fat meal.
There are very few natural foods rich in vitamin D. Fish fat and fish oil contain a lot, but the skin is also produced when exposed to sunlight.
For this reason, vitamin D deficiency is a problem for people who follow an inadequate diet and spend most of their time indoors.
Although it is usually not necessary to take vitamin A, E and K supplements, taking vitamin D supplements is widely recommended.
To get optimal health, make sure you get all fat-soluble vitamins in sufficient amounts.
